Mais buscados:
Energy
Residential
Business
Renew Energy

The power grid in the United States is divided into three systems: Western Interconnection, Eastern Interconnection and ERCOT. Texas is the only state with its system, the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT). It is an organization that works as a broker, managing the power supply to most of the state. It makes sure the power created by generators and the supply is maintained. To find out more about ERCOT and its role in this deregulated energy market, continue reading the post.
ERCOT stands for The Electric Reliability Council of Texas. It is a non-profit organization with a council membership ruled by a board of directors oversight by the Public Utility Commission of Texas and the Texas Legislature. It functions as Texas electric grid operator and schedules the flow of electricity to millions of households in the state, more than 26 million customers, which covers about 90 percent of the state’s electric load.
As the region’s Independent System Operator (ISO) and the first one in the US, ERCOT schedules power on an electric grid that connects more than 52,700 miles of transmission lines and 1,100 generating units. Also, ERCOT´s main responsibilities are managing the reliability of the Texas power grid, overseeing the competitive wholesale market, the retail market and ensuring open access to transmission lines. ERCOT’s members include:
ERCOT manages a competitive electricity market, helping to determine electricity prices based on supply and demand. Also, it monitors electricity generation and demand and takes measures to avoid blackouts or overloads on the grid, ensuring that there is sufficient generation capacity to meet future electricity needs in Texas and promoting energy efficiency.
At the turn of the 20th century, Texas chose to have its power grid, and it is independent from the two extensive power grids in the country: Western Interconnection and Easter Interconnection. The main source of energy for its electric grid is natural gas and, according to ERCOT, the state has the largest amount of energy wind capacity in the U.S. That represents almost 30% of the state’s power capacity. So, natural gas and wind power generate most of the electricity in Texas.
Nowadays, most of the Texas electricity market is deregulated. This means that homes and businesses in this region have the power to choose which energy company supplies their electricity on an open market. There is a theory behind a deregulated market that it would increase competition between energy companies, resulting in more options, lower prices and better plan options for customers (what has been shown in the last years).
ERCOT was founded in 1970 by the Texas Interconnected System, the state utility operator. It was created by then to oversee the reliability and safety of the transmission of electricity. In 1996, ERCOT became the country’s first Independent Service Operator. It manages the grid without owning any assets and began managing wholesale competition on the grid.
ERCOT’s role in Texas later grew under then-Governor George W. Bush. At the time, state lawmakers were considering moving both electricity and telecommunications to a competitive market. The goal was to bring lower prices to customers across the state.
H2: ERCOT’s Unique Structure
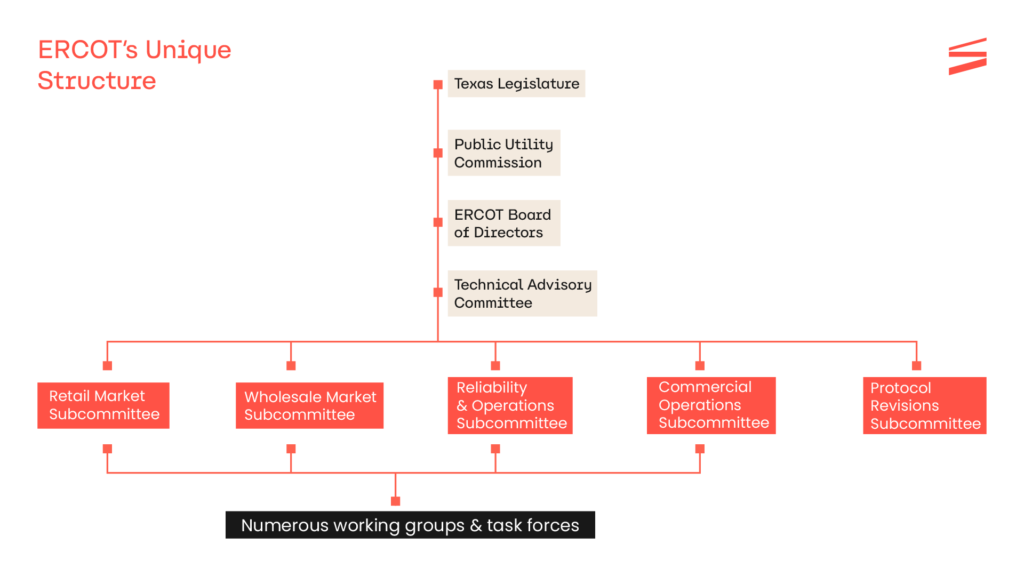
To manage electricity supply and demand, ERCOT has a series of measures:
The Public Utility Commission of Texas (PUCT) has jurisdiction over activities conducted by the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT). ERCOT is governed by a Board of Directors made up of independent and ex-official members.
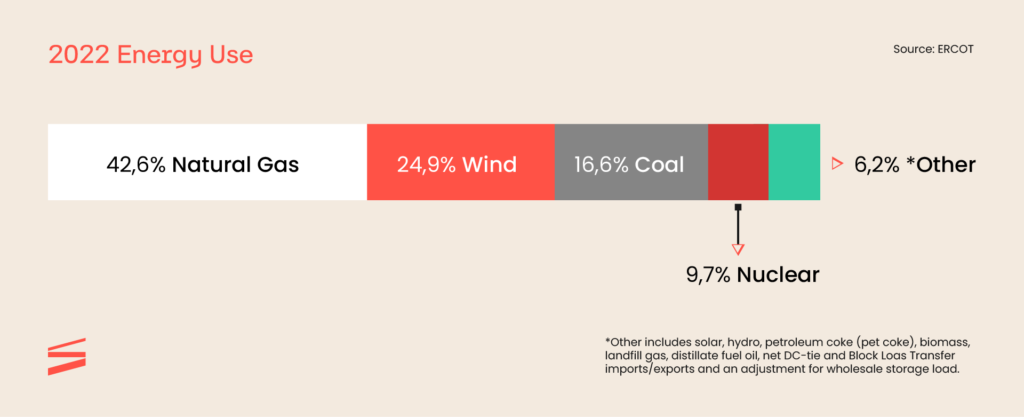
The Lone Star State has a diversified energy matrix. Texas has an abundance of renewable energy resources, and it is a pioneer in wind generated electricity and is among the leading states in solar energy potential. The state will increasingly benefit from these cleaner resources of energy. For instance, solar and wind energy were essential during the heat wave, as they kept Texas power grids running.